Discover the featured content in this month’s The Annals of Thoracic Surgery issue, personally selected by Editor-in-Chief Dr. Joanna Chikwe & Senior Editor Dr. Robbin Cohen, who highlight the authors' important findings, with select illustrations from Dr. Sarah Chen, Associate Editor/CMI. As an additional benefit to your STS Membership and Annals subscription, this monthly newsletter aims to bring expert perspectives on recently published research, straight to your digital doorstep.
Featured in the March 2026 issue...
STS Document | The Society of Thoracic Surgeons General Thoracic Surgery Database: 2025 Annual Update
Alex, David, and coauthors
This annual update of the STS General Thoracic Surgery Database (GTSD) reflects continued growth and utility of the world’s most comprehensive thoracic surgery registry. The GTSD has grown to include more than 800,000 records from over 300 participating sites. The user interface has improved with a major revision of the data collection form and web-based risk calculators for pulmonary resection and esophagectomy. While the database has expanded to include long-term survival data and neoadjuvant therapy use, the star rating system has been retired in lieu of new efforts to define and report quality. For clinical investigators, there are three avenues to obtain GTSD data: the Access & Publications program, the Participant User File, and the Task Force on Funded Research.
-Robbin Cohen, MD, MMM
Senior Editor
Lung | Misinformation and Overestimation of Computed Tomography Lung Cancer Screening Harms—Methodology Matters: A Joint Statement from The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the American Society for Radiation Oncology, and the American College of Radiology
Tupper, Servais, and coauthors
The authors criticize the methodology used by recent publications that they feel inaccurately overestimate the harms of lung cancer screening (LCS) with CT scans. These include studies that report higher rates of downstream imaging and complication estimates when compared with the National Lung Screening Trial, studies that misreport the LCS false positive rate (FPR) by mislabeling the false-discovery rate as the FPR, and studies that overestimate the oncogenic risk of serial CT imaging. The authors emphasize that disseminating inaccurate information regarding LCS fuels “unwarranted fear of overdiagnosis, overtreatment, and iatrogenicity,” deterring patients from seeking its proven benefits.
-Robbin Cohen, MD, MMM
Senior Editor
Aorta | Late Aortic Reinterventions After Surgery for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection
Bjurbom, Olsson, and coauthors
This retrospective single-center study looks at aortic reintervention in 225 patients who underwent surgical repair for acute type A aortic dissection (ATAAD) with >10-year follow-up (median 10.3 yrs, range 5-13.4 yrs). First aortic reintervention occurred in 37 patients (16.4%) at a median of 7.9 years after the index repair, with a second reintervention in 12 patients, and a third in 2 patients. The most common indications for reintervention were aortic dilatation (84%) and aortic regurgitation (27%). Factors associated with proximal reintervention (usually aortic root replacement) were root diameter >45 mm without root replacement at index repair and bicuspid aortic valve. Factors associated with distal aortic reinterventions (open or endovascular) were failure to completely resect the primary repair and connective tissue disorders. There was no perioperative mortality.
-Robbin Cohen, MD, MMM
Senior Editor
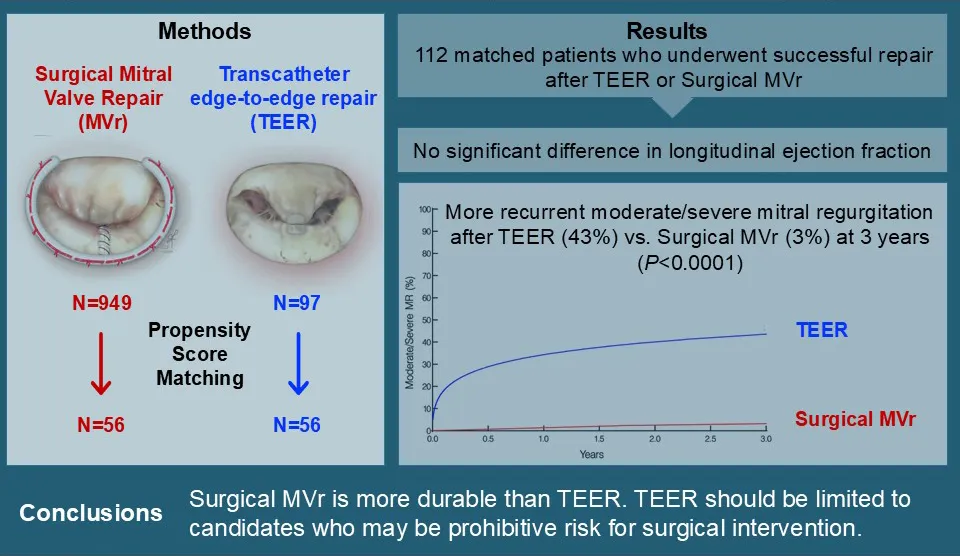
Valve | Durability of Surgical Mitral Repair vs Transcatheter Edge-to-Edge Repair in Patients With Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation
Bakir, Gillinov, and coauthors
Surgical repair provides superior midterm repair durability over transcatheter mitral repair in patients with degenerative mitral regurgitation caused by posterior leaflet prolapse.
-Robbin Cohen, MD, MMM
Senior Editor
Policy & Ethics | Evaluating Gender Disparities in Cardiothoracic Surgery through the Lens of Industry-Surgeon Partnerships
Yang, Ha, and coauthors
This was an analysis of the Open Payments Database (OPD) from 2016-2022, examining federally reported industry payments to cardiothoracic surgeons. There were 417,530 payments ($230,304,205 total) made by 829 companies to 5971 CT surgeons. Female surgeons received only 2.2% of total payments, though this improved from 1.8% in 2016 to 7.7% in 2022. Female surgeons participated in significantly fewer transactions and earned less per transaction than their male colleagues. They were also underrepresented in consulting and education-related transactions compared with other categories.
-Robbin Cohen, MD, MMM
Senior Editor
Congenital & Pediatric | Melody vs Mechanical Mitral Valve Replacement in Young Children: A Single-Center Propensity Matched Analysis
Moroi, Goldstone, and coauthors
This retrospective review used propensity score matching to compare the Melody valve (Medtronic Inc); a stented, balloon-expandable bovine jugular vein valve, with mechanical MVR in 36 children <2 years old (median age 5.2 months) with biventricular physiology. Operative techniques are described. Twenty-eight patients (77.8%) had a prior sternotomy, with 26 patients (72.2%) having undergone prior MV repair or AV septal defect repair. Despite a high rate of early surgical reinterventions in both groups (16%), there were no differences in surgical reintervention at 2 years (Melody: 32.2%; Mechanical: 30.3%; P = .3), or transplant-free survival at 5 years (Melody: 66.7%; Mechanical: 66%; P = .96).
-Robbin Cohen, MD, MMM
Senior Editor
Valve | Outcomes of Re-Repair vs Replacement After Failed Primary Mitral Regurgitation Repair: The Society of Thoracic Surgeons Adult Cardiac Surgery Database Analysis
Ibrahim, Szeto, and coauthors
The STS Adult Cardiac Surgery Database was utilized to study 1749 patients who required reoperation for mitral regurgitation after isolated repair for degenerative mitral regurgitation between 2011 and 2023. There were 410 re-repairs (23.4%) and 1339 mitral replacements (76.6%). Most patients underwent re-operative mitral surgery within 2 years of the initial procedure, with a shorter time to reintervention for patients undergoing re-repair than replacement (521 days vs 751 days; P < 001). Unadjusted overall survival was better for patients undergoing re-repair vs replacement. This survival benefit persisted after risk adjustment and propensity score matching. Re-repair patients also had lower postoperative morbidity or mortality (6.8% vs 11%; P = .042). In his invited commentary, Dr Tirone David discusses the technical aspects of primary mitral valve repair that lead to failure and their solutions.
-Robbin Cohen, MD, MMM
Senior Editor
Congenital & Pediatric | Surgical Approaches in Congenital Heart Disease With Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: A Multiinstitutional Analysis
Holden, LaPar, and coauthors
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is associated with congenital heart defects (CHDs) in 10-35% of cases. The authors queried the CDH Study Group registry (CDHSG) to analyze outcomes and decision making in patients with CDH and CHD. Of 9261 patients with CDH, 1886 had CDH + CHD, and 209 (11%) underwent both cardiac and diaphragm repair. Ninety-four percent underwent diaphragmatic repair before the cardiac operation, with most subsequent CHD operations occurring 30-80 days after CDH repair. Overall mortality was 23.4%. Extracorporeal life support was a significant predictor of in-hospital mortality (odds ratio, 5.74; P = .001). When stratified by STAT category, patient mortality correlated with CDH Study Group stage.
-Robbin Cohen, MD, MMM
Senior Editor
Mediastinum & Esophagus | Comparison of Oncologic Outcomes After Partial and Total Thymectomy for Stage I Thymomas
Campbell, Louie, and coauthors
The International Thymic Malignancy Interest Group retrospective database was utilized to compare total thymectomy (TT, 534 patients) with partial thymectomy (PT, 158 patients) for stage 1 thymomas without myasthenia gravis. PT patients were younger, had better performance status, and more T1b histology. PT patients had statistically similar recurrence and survival, and no difference in the development of new-onset myasthenia gravis compared with TT.
-Robbin Cohen, MD, MMM
Senior Editor
